Car seat safety
While I have always known the importance of car seats for the safety of our little ones, it wasn’t until I found myself struggling to install one at nine months pregnant that I realized how many questions I had about them! There are ones for newborns and ones for older children. Should I have gotten the one that stays in the car or is the one that clicks in better? Some are simple and some have many features, and boy, can they range in price! Should I install it on the passenger side, driver side, or in the middle? There are laws about rear facing and front facing–and how on earth do I know if I actually installed it correctly? Here are some of my questions answered.
What is the law?
The Pennsylvania Child Passenger Safety Law was updated this past August. Children who are under the age of two must remain rear facing in their car seats. It is recommended that once children reach two years or older they should remain rear facing until they outgrow the height and/or weight limits set by the car seat manufacturer.
Why rear facing?
Frontal crashes are the most common type of automobile accident. When a child is in a front-facing car seat (FFCS) during a frontal crash, the child is thrown forward, propelling the child in the opposite direction of the car seat risking injuries or even death. When the child is in a rear-facing car seat (RFCS) during a frontal crash, the child is pushed back into the car seat rather than away from it. Simply put, having the car seat rear facing allows the child to be supported against the forward motion caused by a frontal crash.
In 2007, a study used data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to compare the risk of injury for children under the age of two in a RFCS versus a FFCS. The study used fifteen years of data, covering the years 1988 to 2003. Findings concluded that ,“Regardless of the age group considered, RFCS use resulted in lower risk of injury than FFCS use for crashes of all directions.” (Henary, B et al.)
How do I choose a seat?
When choosing a car seat, consider your child’s height and weight. Car seat manufacturers place height and weight limits on the seats for safety reasons, which vary by the type of seat. There are some seats designed specifically for infants and others that convert through stages of growth.
Some seats remain in the car at all times and others have a base that stays attached to the vehicle while the seat can be lifted out. This is usually the case for infant car seats. Some detachable car seats may offer further options, such as locking into a complimentary stroller, a convenience for which many parents may be willing to pay the extra cost.
While web searches are great for narrowing your choices, you may wish to check out some car seats in person. They vary in color, fabric, and how they install in the vehicle. You may be able to wipe some to clean, while others have covers you can remove and throw in the washing machine. Some car seats are installed using your vehicle’s seatbelts while others have options for a LATCH system, clips that latch into specific anchors in your vehicle. Not all vehicles are equipped with the LATCH system, so be sure to check your car’s Owner’s Manual to see if your vehicle is equipped for a LATCH system or if your vehicle recommends a specific kind of car seat.
Find additional resources to help you choose here.
How do I know if I have installed the car seat correctly?
Begin with your car’s Owner’s Manual, which may recommend where to place the car seat. For some vehicles, it is not safe to have the car seat in the middle of a row, depending on if the seat is flush or has a rise in it. Your Owner’s Manual will also provide any other recommendations specific to your vehicle. Though the middle of the rear seat can be a safe place for the car seat, I found out when reading my Owner’s Manual that this is not the case for my vehicle because the center seat was higher than the others. You will also learn if your vehicle has a LATCH system and where the anchors are.
Next, read thoroughly and follow the instructions provided by the car seat manufacturer. Some seats should be placed in a specific position depending on if they are rear- or front-facing. Some seats have a level indicator. The Instruction Manual will guide you through the installation.
There are also many specific scenarios such as where to install a car seat in a pick-up truck with only one row of seats, or where to mount a third car seat in a sedan with two other car seats already installed.
Whether you are in one of these situations or just want to feel more at ease, you can find a local car seat check station here, or here. Trained techs can provide educational services to ensure the seat is installed correctly. You can use one of the links below to find an event or inspection station. You can also contact your local Emergency Medical Services, Fire, or Police stations to find out if they offer checks or safety events. My local police station provided checks on certain days of the week by appointment.
Video resources are also available from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
How do I know if my child is fastened in correctly?
- Carefully follow the instructions provided by the car seat manufacturer. Be sure that safety harnesses are fastened and tightened snugly. Determining this is one of the things I found most difficult until I learned about the “pinch test.”
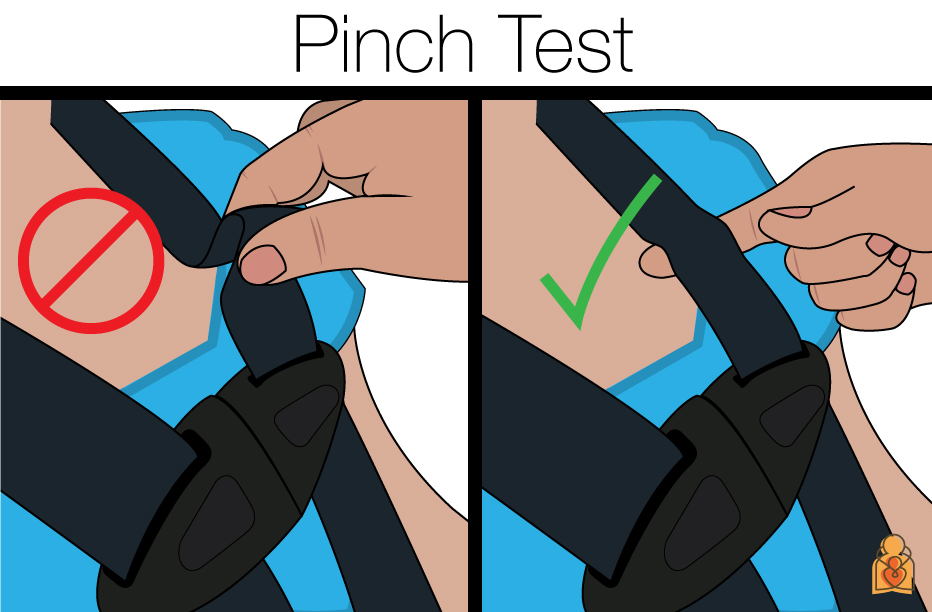 Image from Healthychildren.org
Image from Healthychildren.org - Be sure that the harnesses are at the correct position or height behind the shoulders. This varies with the size of your child.
- Ensure the chest clip is at armpit level.
- Do not fasten in your child wearing bulky clothing such as winter jackets or snowsuits. This prevents the harnesses from being properly secured, and your child can actually slip through them in a crash. Again, you can visit a check station for education about properly securing your child. Check Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh’s Car Seat Check Schedule, or a PA Techs fitting station for more information.
What about recalls?
Car seats have expiration dates and may also be recalled for safety reasons. Never use a car seat that doesn’t include the manufacturer’s manual. Recalls can be found by calling the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration or visiting their website.
Car seat accessories
From mirrors and toys to puffy shoulder pads and headrests, there are an abundance of car seat accessories. None of them, however, are recommended. Additional padding or inserts from the car seat manufacturer are the only accessories that were crash tested with that specific seat. Adding other accessories may prevent the harnesses from being secured in the proper position or risk injury to the child if they would become dislodged in an accident.
If you are concerned about how your child fits into the car seat, seek education from a certified tech.
Car Seat Guide from Children’s Hospital of UPMC
Sources:
Car Seats: Information for Families. (n.d.). Retrieved September 26, 2016, from https://www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/on-the-go/pages/Car-Safety-Seats-Information-for-Families.aspx?gclid=CKPmrdSgs88CFYEehgod0roNWg
Henary, B., Sherwood, C. P., Crandall, J. R., Kent, R. W., Vaca, F. E., Arbogast, K. B., & Bull, M. J. (2007). Car safety seats for children: Rear facing for best protection. Retrieved September 26, 2016, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2598309/
Rear-Facing Car Seats for Infants & Toddlers. (n.d.). Retrieved September 26, 2016, from https://www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/on-the-go/Pages/Rear-Facing-Car-Seats-for-Infants-Toddlers.aspx
Rear-Facing: Why It’s Beneficial. (n.d.). Retrieved September 26, 2016, from http://www.preventinjury.org/Child-Passenger-Safety/About-Child-Safety-Seats/Rear-Facing-Why-It-s-Beneficial




